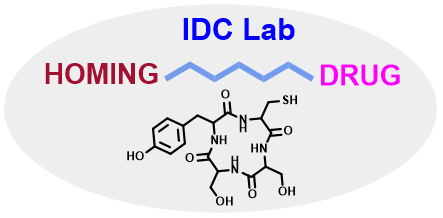
Nature Cyclic Peptides-Inspired Payloads
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are a novel cancer treatment that combines the specificity of monoclonal antibodies with the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs. This targeting strategy selectively destroys cancer cells while protecting healthy tissues. This targeting mechanism has shown impressive clinical efficacy in the treatment of various malignancies. Future developments in this field are likely to focus on enhancing linker technology to improve stability and modulate the release of cytotoxic drugs, incorporating novel, more potent cytotoxic drugs, and identifying new cancer-specific antigens through genomic and proteomic technologies. Many natural or nature-inspired organic molecules are known to have interesting anticancer properties. We are very interested in developing payloads of novel anti-tumour mechanisms, especially natural cyclic peptide molecules with anti-tumour activity.
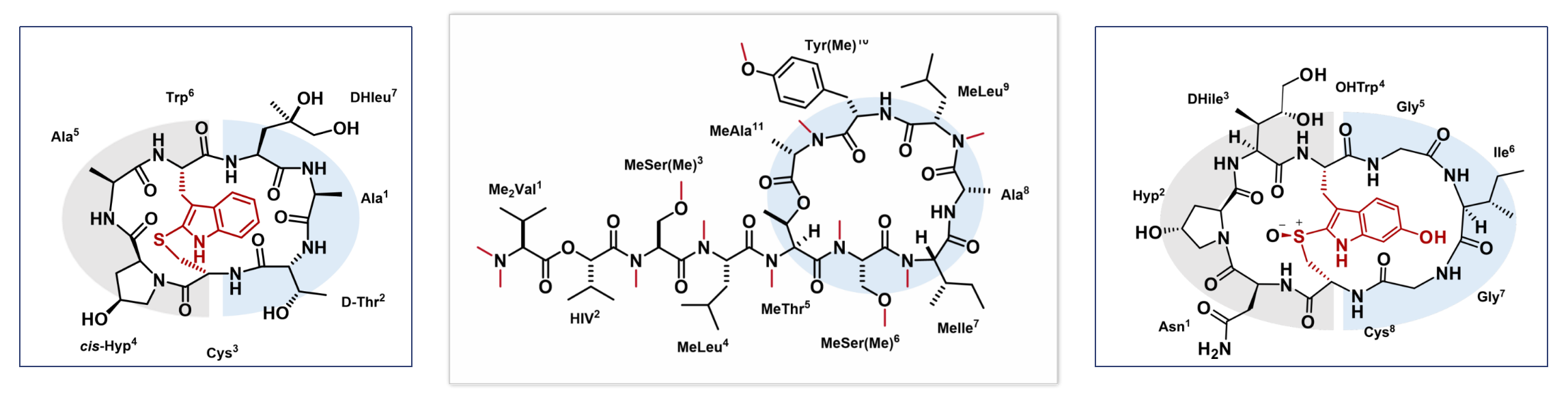
Conformational Space of Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides offer a promising scaffold for the development of new drugs, in part due to their rigid conformation in comparison to linear peptides. Nevertheless, the complex cyclic structure presents a significant challenge in optimising the target-binding affinity and the pharmacokinetic characteristics. In recent years, a number of new conformational isomers have been identified, prompting chemists to direct their attention towards the stereoselective synthesis of these compounds, which can be achieved through the utilisation of intramolecular hydrogen bonding interactions and pre-organised structures. However, the interconversion between conformational isomers presents a challenge in evaluating the biological activity of peptide drugs. Our group is particularly interested in exploring the chemical space of cyclic peptides.
Peptide Drug Conjugates
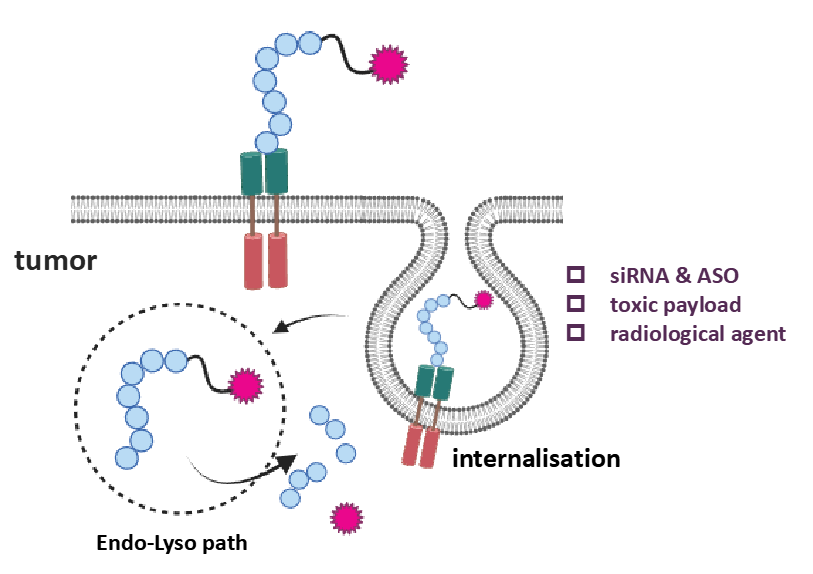
Peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) represent the next generation of targeted therapeutics following antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), offering the advantages of enhanced cell permeability and improved drug selectivity. Our focus is on the development of high-throughput cyclic peptide screening technology in combination with artificial intelligence to optimise the targeted delivery of cyclic peptide molecules through organic chemistry. This initiative is designed to provide a platform for the precise targeted delivery of peptide-coupled nucleic acid drugs, peptide-coupled radiopharmaceuticals and peptide-coupled toxin molecules.